Discover Lean Healthcare and its models, including TPS, Six Sigma, and Lean Six Sigma, to streamline workflows, reduce waste, and enhance patient care.
Every second matters in hospitals. Nurses dash from one room to another, physicians confer over pressing cases, and patients eagerly await their time. Lean Healthcare and Its Models brings a sense of order to the chaos and transforms the delivery of care.
Imagine a patient coming into the Emergency Room with acute stomach pain. In a traditional hospital, they would have to wait hours, endure redundant paperwork, and get lost between departments. But in lean healthcare, the patient is rapidly evaluated and referred to a specialized team that uses established protocols to minimize delays.
Discover how our AI-powered medical billing and scribe solutions can help your healthcare practice achieve greater efficiency. Learn more here.
At Its Core, Lean Healthcare is Built on a Few Key Ideas:
Prioritizing What Counts: The aim is to provide patients with the optimal care while eliminating anything that is not needed. Healthcare workers are encouraged to always seek out and remove activities that do not contribute value.
Getting to Know the Patient’s Journey: By charting out each step a patient makes from the time they arrive until the time they leave, it is evident where improvements can be made.
Reducing Waste: Whatever is not beneficial to the patient is waste—such as waiting for a long time, unnecessary movement, or redundant work. Lean practices assist healthcare systems in detecting and getting rid of such wasteful practices in a scientific manner.
Always Getting Better: Lean Healthcare and Its Models is a continuous process. It is a matter of discovering new ways to improve, implementing them, and observing how well they function. It is a continuous endeavor to deliver better outcomes to patients.

Overview of Lean Healthcare
The concept of ‘lean’ originated in manufacturing. John Krafcik pioneered the use of the term in 1988. Subsequently, in 1996, James Womack and his colleagues defined it more comprehensively as a method of continuous improvement by eliminating unessential activity and concentrating on what is required by customers.
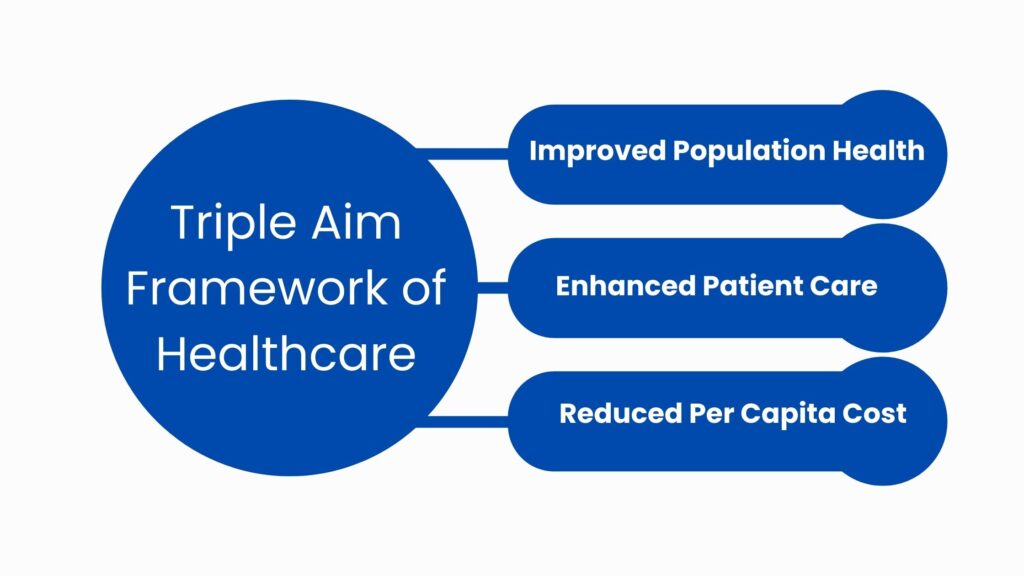
In America, the Institute of Health Improvement developed the Triple Aim. It’s a model that enables healthcare organizations to enhance three things simultaneously: patients’ perceptions of care, the health of populations, and the cost of care per individual.
Although there are established methods for applying lean, every organization must tailor these techniques to its own circumstances. To be successful, all members of the organization must be dedicated to continually looking for ways to make things better. When properly executed, lean healthcare can significantly improve the way care is provided.
Here are Some of the Definitions of Lean Healthcare by Different Authors:
Black and Miller (2008)
❝Lean healthcare is a patient-focused approach to managing and delivering care that continuously improves work processes. All aspects of the care delivery system are focused on eliminating waste while steadily increasing value-added work. It is premised on the idea that healthcare can be continuously improved without adding more money, staff, space, or inventory.❞
Simply put, Black and Miller describe lean healthcare as a way to prioritize patients. It’s about making healthcare processes better by cutting out unnecessary steps and focusing on what truly helps patients. The key is to improve how things are done, not just by adding more money, staff, or space. This approach shows that we can make healthcare better by doing things smarter, not just by using more resources.
Poksinska (2010)
❝Lean healthcare involves understanding what adds value for patients and eliminating waste from care delivery. It often emphasizes that current healthcare systems have fragmented, inefficient processes that require redesigning the flow of patient care.❞
Poksinska stresses that lean healthcare is all about determining what is most important to patients and eliminating anything that wastes time or is not helpful. She adds that most healthcare systems now have processes that are slow or broken, and these must be streamlined to enhance patient care.
D’Andreamatteo, Lanni, Lega and Sargiacomo (2015)
❝Basic Principles – Specify value from the patient’s perspective, map the value stream, enable uninterrupted workflow, allow patients to pull value, and continuously improve.
Other Principles – Involve all staff in improvement, respect all employees, and integrate suppliers into the value stream.❞
These authors share some key ideas about lean healthcare. The main points are:
Focus on what matters to patients: Understand what they need and value.
Map out how to deliver that value: Clearly outline the steps to provide good care.
Keep things moving smoothly: Make sure the workflow is efficient.
Let patients start the process: Allow them to initiate their care when needed.
Always look for ways to improve: Keep working on making processes better.
They also emphasize other important principles: involve everyone in making changes, treat workers with respect, and include suppliers in the process of delivering value to patients.
Waste Categories Used in Lean Healthcare
Defects
Mistakes are possible in medical procedures due to incorrect diagnoses or defective equipment requiring maintenance. Such problems can escalate costs, cause injury to patients, and prolong care. For example, if a patient is wrongly diagnosed, they may receive the wrong therapy. This may result in serious medical issues and increased medical costs.

Overproduction
When we make more medical devices and medicine than we require, it results in waste. This waste may be in the form of unnecessary tests or treatments that do not benefit patients. For instance, performing too many blood tests on a patient when they are not required wastes resources and contributes to healthcare expenses.
Waiting
When patients wait longer to see a doctor, receive test results, have access to medical equipment, or undergo consultations, it can cause extended hospital stays. This may also result in patient satisfaction being neglected. For example, a patient waiting hours in the Emergency Room to be seen by a doctor may be uncomfortable and unhappy.
Non/Underutilized Talent
When medical personnel are not applying their knowledge and skills optimally, there are a lot of issues. There can be errors, and morale among staff may decline, meaning they are unable to perform their best. For example, a nurse with special training in wound care may find themselves doing paperwork such as logging patient visits and discharges rather than concentrating on assisting patients with their particular needs.
Transportation
Transportation waste in the healthcare setting is defined as the transportation of patients, employees, or medical equipment around without a valid reason. For instance, transporting a patient several times for tests can be unnecessary and present issues. It can raise the risk of error and make the patients more uncomfortable.
Inventory
Having too little or too much healthcare supplies and medicines can be detrimental to patient care. Too many supplies may mean that some of them expire before they are utilized, which is a waste of money. Too little, however, leads to delays in treatment. For example, if medical stock expires before it is utilized, it amounts to loss of money. Furthermore, treatment delays due to shortages can have serious implications, even life-threatening.
Motion
If workers are required to move around extra distances, then this can squander time and decrease their effectiveness. This, in turn, can result in reduced patient care. For instance, if the nurse spends ample amounts of time locating the blood pressure machine instead of attending to the patients about their issues, then it is likely to compromise the entire team’s productivity.
Extra or Over-Processing
Performing unnecessary tasks, such as additional tests, can drive medical expenses up and delay patient care with no resultant benefit. Examples include repeating the same patient details on several different treatment forms that can result in additional errors and additional work for healthcare professionals.
Six Principles of Lean Healthcare
When applying lean healthcare principles, collaboration is important. Healthcare practices must concentrate on enhancing the way they apply these principles. They must identify areas of improvement and apply data to inform them. Through the application of lean healthcare concepts, your clinic can establish a stable setting that provides high-quality care without waste.
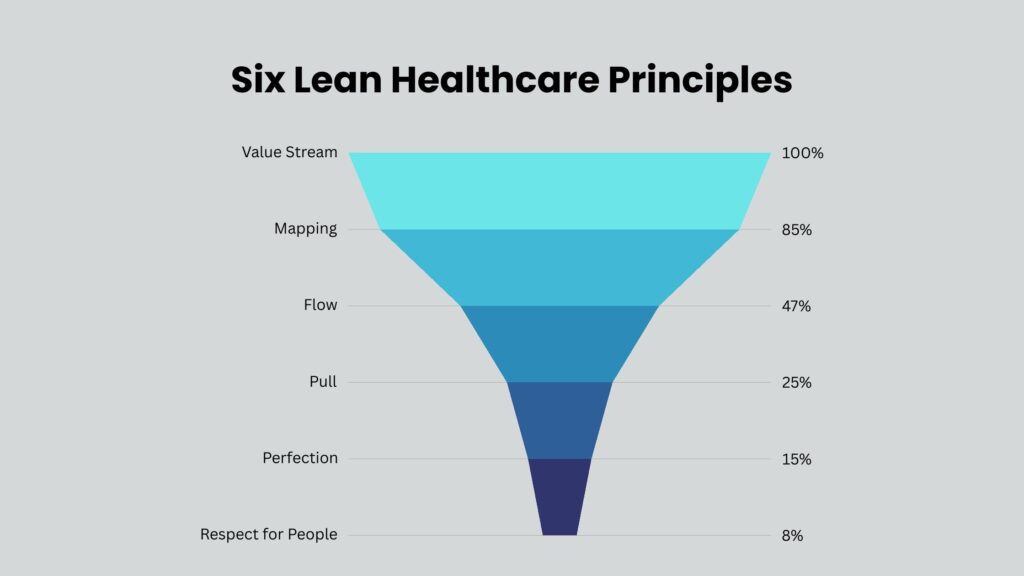
Value:
Knowing what is most important to patients is crucial. This philosophy is all about delivering healthcare services that enhance patient care and put smiles on patients‘ faces. By concentrating on what patients require, we can cut out things that are not necessary and maximize their experience.
Value Stream Mapping:
This process demonstrates all the steps involved in patient care, from admission to discharge. It allows health professionals to detect and eliminate waste, so the whole process runs more smoothly and patients progress through the system unproblematically.
Flow:
This principle guarantees all healthcare processes function efficiently without breaks. It manages the flow of patients, information, and medical supplies. Without delays and issues, healthcare practices can minimize wait times and enhance services.
Pull:
A pull system delivers healthcare services according to patient requirements, not predetermined timetables. This method avoids overproduction and ensures efficient utilization of resources, resulting in quality patient care and resource utilization.
Perfection:
This principle is related to constantly seeking methods of improving healthcare processes. It stresses the need for continuously monitoring and improving quality, minimizing errors, and being more efficient. It inspires healthcare professionals to look constantly for better ways of doing things.
Respect for Everyone:
Valuing the work of all healthcare professionals is important for ensuring high standards of care. This value should be used to establish a work culture that fosters a good environment where everybody feels motivated to contribute ideas toward process improvement. When healthcare institutions have a positive culture, they are able to improve patient care and make employees happier.
Do You Know- What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is an effective method to enhance healthcare processes and patients’ happiness. It merges two methods: Lean, which tries to remove waste and optimize operations, and Six Sigma, which seeks to decrease errors and increase quality. Lean applies tools such as recognizing the 8 Wastes and the PDCA cycle (Plan, Do, Check, Act). Six Sigma employs the DMAIC approach, which means Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control.

Imagine it as a productive garden in which every plant has a function within the system. Lean and Six Sigma interact to assist healthcare practices to provide improved care. They improve performance, reduce waste, and make quality consistently meet high levels.
Lean Methodologies and Implementation in Healthcare
Lean principles are essential to enable improved patient care, streamline healthcare operations, and eliminate waste. Some of the practices that facilitate improvement in the healthcare system include:
Value Stream Mapping (VSM):
Value stream mapping is a valuable tool for healthcare organizations to improve patient care. It provides a clear picture of the whole process of taking care of patients from beginning to end. It includes every task, such as ordering supplies and administering medicine. The map allows teams to spot problems, waste, and inefficiency so that they can eliminate them. This easy process saves money and wait times, making care improved.
How Value Stream Mapping Works in Healthcare
Healthcare professionals make a value stream map by examining each phase of the patient’s experience. This illustrates which steps provide value and which do not. Value-added steps assist patients to recover, such as tests to identify problems and treatments to assist recovery. Non-value-added steps are actions that waste time and do not enhance care, including waiting for an appointment or filling out extensive forms.
With this picture, healthcare teams are able to reimagine workflows with an eye towards the activities that create value and eliminate waste. Patients get quicker, better care. Providers gain reduced costs and more effective use of resources. It’s a win-win for all through wiser care delivery.
Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)
Kaizen is a method of continually seeking means to make things better. It is where all members of an organization come together to implement small improvements daily. The aim is to cut waste and make processes more efficient.
In healthcare, Kaizen can be used to enhance the process of patients navigating through a clinic. A group maps out each step of the patient’s experience, from check-in to the doctor and check-out. They spot troubles or bottlenecks at each phase and work on ideas that simplify the process. This can be as low key as switching up furniture arrangement or posting up signs. Kaizen is less about making overall drastic changes, rather than continuously tweaking small modifications.
How Kaizen Works in Healthcare
Kaizen requires all healthcare personnel to contribute suggestions for enhancing the care and satisfaction of patients. Every day, a brief team meeting can be conducted to touch base on matters from the preceding day and probable solutions. In addition, staff can use a suggestion box anonymously to contribute ideas.
Kaizen implementation entails building a culture in which everyone is continually learning and enhancing. Leaders should be receptive to input from all employees, including technicians, nurses, billing clerks, and so on. Frequent, tiny changes proposed and piloted by frontline workers will often make the greatest difference.
Just In Time (JIT)
The Just In Time approach is to obtain supplies and materials only when you require them, as opposed to stockpiling in advance. The aim is not to have too much inventory, which can be wasteful. With JIT, you produce or order precisely what you require, precisely when you require it. This saves money and makes things more efficient.
How JIT Works in Healthcare
Healthcare professionals can utilize the JIT approach to control drugs and supplies. Rather than keeping large reserves of additional supplies in anticipation of what may be needed in the future, healthcare facilities can purchase drugs and medical supplies based on what they actually use on a daily basis. For instance, a clinic pharmacy can monitor the number of prescriptions filled for certain drugs on a day-to-day basis. It can then reorder from suppliers to cover this usage. This avoids over-ordering and out-dated drugs. It minimizes the storage requirement and eliminates inventory expense. The most important factor is a clear understanding of the daily requirements and a speedy ordering process.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a problem-solving tool applied in healthcare. It assists in determining the underlying causes of problems. Rather than merely addressing symptoms, RCA entails going deeper to learn why things go wrong in the first place. The aim is to discover methods of avoiding these issues from occurring again.
How Root Cause Analysis Works in Healthcare
Suppose a patient receives the incorrect dose of medication. RCA assists the healthcare team to inquire into what happened. They may learn that drug labels were confusing, nurses had too much work to do, or staff members were confused. Once the root cause is determined, hospitals can implement specific modifications, like changing labels, changing nurse schedules, or enhancing information transmission between staff. This precludes such medicating errors from occurring in the future and enhances patient safety.
Kanban (Card You Can See)
Kanban is one method of visualizing and organizing work as it progresses from one stage to another. Kanban employs cards or signs to represent tasks or pieces of work and how they move from beginning to completion. The primary intention is to observe the workflow, restrict the amount of work being done at a time, and optimize it. Picture a board with sticky notes traveling across columns to monitor when something is in waiting, in process, or complete.
How Kanban Works in Healthcare
Kanban cards can be used by hospitals to follow patients from one department to another. A card might track a patient’s path from arrival to receiving tests, undergoing surgery, and recovery. This provides employees with an easy means of viewing where the patients are and what is yet to be done.
For supplies, color-coded cards can be used to show when surgical instruments or medications are low. This alerts staff to what needs to be reordered, so they don’t overstock. Patients receive what they need, when they need it, without supplies sitting idle on shelves.
Poka-Yoke (Error Proofing)
Poka-Yoke is a lean strategy that prevents errors from occurring in the first place. It’s all about designing quality into processes by introducing simple checks that make mistakes nearly impossible. The concept is to create systems where the next action is always the correct one. This way, you don’t require costly checks and inspections down the line.
How Poka-Yoke Works in Healthcare
Poka-Yoke can be used by healthcare organizations to minimize medical mistakes that endanger patients. For instance, via barcode scanning to provide patients with the correct medication and dosage, or during surgery using checklists to ensure all instruments are present. There are also alarms that sound when the incorrect dosage is inputted for IV pumps. The straightforward devices make it more difficult for personnel to commit errors that can injure patients.
Poka-Yoke shifts the emphasis from blaming people for errors to designing systems that eliminate errors in the first place. This builds a safety and continuous improvement culture in healthcare. When errors can’t occur, patient outcomes improve and costs decrease.
Heijunka (Production Leveling)
Heijunka is a lean approach that helps spread out work evenly over time. It’s about balancing the types and amounts of tasks across different periods. The main goal is to get rid of unevenness, overwork, and waste. By doing this, Heijunka creates a steady and predictable pace, allowing operations to run at just the right volume. This reduces variability and stress on the system.
How Heijunka Works in Healthcare
Heijunka can actually assist healthcare professionals in better managing their workload. It is about planning carefully the kinds and quantities of procedures during the week or month. This smoothes out the workflow so that you don’t have massive backlogs on certain days and blank schedules on others. For example, a surgeon can stagger surgeries rather than clumping them all into a few days. This keeps staff from becoming overwhelmed during hectic days and lessens patient wait times because work is distributed predictably. Heijunka keeps healthcare teams functioning at an enjoyable rate.
What is 5S Methodology in Lean Healthcare?
Examples of Lean Healthcare
Here are a few simple illustrations of how lean healthcare can facilitate easier task management and enhance health care practices:
Example #1- Reducing Wait Times in The Emergency Room
Have you ever spent hours sitting in the emergency room? Lean healthcare can make those waits a thing of the past. Hospitals employ a process called Value Stream Mapping to map out every move a patient makes from arrival through discharge. By making processes smoother in the emergency department, hospitals can eliminate wasted time by as much as 30%, putting patients in better moods.
Example #2- Faster Patient Discharges
Discharging patients from the hospital is often a time-consuming, infuriating experience with reams of paperwork and communication breakdowns. Lean healthcare employs a process known as Kaizen, or continuous improvement. Healthcare professionals work together to examine the process of discharge, identify inefficiencies, and implement changes such as pre-discharge planning and electronic documentation. This can cut discharge by 20-40%, allowing beds to be vacated for new patients more rapidly.
Example #3- Faster Lab Test Results
Did you ever have to wait a long time for lab test results before your physician could diagnose you or prescribe medication? Lean healthcare allows labs to implement a “Just-In-Time” system, where they order tests on demand instead of batching large quantities. This makes their processes quicker and returns results 20-30% faster.
Example #4- Reducing Hospital-Acquired Infections
No one wishes to contract an infection during their time in the hospital! Lean healthcare applies Root Cause Analysis to pinpoint the causes of such infections. Hospitals can subsequently apply measures such as enhanced sterilization of equipment and improved hygiene of hands to minimize these damaging infections.
Pros and Cons of Lean Healthcare
You can have a number of advantages by implementing lean healthcare in your practice, but there are some challenges involved, and they can be overcome with effective strategies.
Pros of Lean Healthcare
- Efficiency and Reducing Waste: Lean healthcare eliminates excess steps and streamlines medical processes. This is done by making workflows simpler, managing patient movement, and eliminating unnecessary activities.
- Cost Savings: Lean practices assist in the identification and removal of activities that do not add value, which can greatly decrease operational expenses. This involves decreasing inventory expenses, minimizing wait times, and optimizing the use of resources.
- Enhanced Workplace Culture: Lean healthcare empowers workers to find and fix problems themselves. This can increase job satisfaction and encourage staff to work more diligently.
- Improved Patient Care: Applying lean healthcare techniques guarantees that patients are treated rapidly and efficiently, resulting in contented patients and improved results.
- Improved Patient Safety: Through the application of well-defined processes and good practices, lean healthcare has the potential to minimize the occurrence of errors and enhance patient safety.
Cons of Lean Healthcare
- Cultural Transformation and Resistance: Sustaining lean practices necessitates profound cultural transformations and commitment by healthcare practices. But change resistance and poor support from the staff can complicate success.
- Data Challenges and Complexity: Measuring the effectiveness of lean programs becomes challenging when these are complicated. Operating such systems efficiently calls for improved data analysis and gathering.
- Overemphasis on Efficiency: Too much focus on efficiency can sometimes neglect significant human aspects. Disregarding these aspects may result in burnout among staff and decreased quality of care.
- Sustainability: Sustaining lean healthcare behaviors over the long term can be difficult. Constant monitoring and enforcement are essential to ensure these behaviors continue to function optimally in healthcare.
- Resource Limitations: Small medical practices may struggle with resource management. Going lean on processes may take longer, require more training and capital.
Conclusion
Are you paying attention to how your practice is running right now? Using lean healthcare methods helps you focus on reducing unnecessary steps and making processes smoother. This can lead to better care for your patients. When you put patients first, the quality of care improves, and your medical business becomes more adaptable. By managing patient flow efficiently, you can keep your business profitable while also providing better services.
While Lean Healthcare enhances efficiency, integrating AI-powered solutions takes it to the next level. AI-driven tools can automate documentation, streamline billing, and improve workflow efficiency. Our AI-powered medical scribe solutions at RevMaxx are designed to complement Lean Healthcare by reducing administrative burden and enhancing real-time documentation.
For a deeper dive into Lean methodologies in healthcare, check out this comprehensive guide on our sister website , revmaxx.